House Ways and Means Median Family Income 2017
| | Parts of this commodity (those related to documentation) need to exist updated. (September 2020) |

Median Usa household income through 2019

U.S. real median household income reached $63,688 in Jan 2019, an increase of $171 or 0.3% over i calendar month (December 2018) .[1]

Household income is an economic standard that can be applied to one household, or aggregated across a large group such as a county, city, or the whole state. It is commonly used past the The states government and private institutions to describe a household's economic status or to rails economical trends in the US.
A key measure of household income is the median income, at which one-half of households have income above that level and half below. The U.S. Census Bureau reports two median household income estimates based on information from ii surveys: the Current Population Survey (CPS) and the American Community Survey (ACS). The CPS is the recommended source for national-level estimates, whereas the ACS gives estimates for many geographic levels.[2] : 19 [three] : 10 According to the CPS, the median household income was $63,179 in 2018.[2] [4] Co-ordinate to the ACS, the U.Due south. median household income in 2018 was $61,937.[3] Estimates for previous years are given in terms of existent income, which have been adjusted for changes to the price of goods and services.
The distribution of U.S. household income has become more unequal since around 1980, with the income share received by the top 1% trending upwardly from around 10% or less over the 1953–1981 period to over 20% past 2007.[5] Later on falling somewhat due to the Nifty Recession in 2008 and 2009, inequality rose once again during the economic recovery, a typical pattern historically.[6] [7]
Definition [edit]
A household's income can exist calculated in diverse ways but the US Census every bit of 2009 measured it in the following way: the income of every resident of that house that is over the historic period of 15, including pre-revenue enhancement wages and salaries, along with whatsoever pre-revenue enhancement personal business organization, investment, or other recurring sources of income, as well as whatsoever kind of governmental entitlement such every bit unemployment insurance, social security, disability payments or child support payments received.[viii]
The residents of the household do not have to exist related to the head of the household for their earnings to be considered part of the household's income.[ix] Equally households tend to share a like economic context, the use of household income remains among the most widely accustomed measures of income. That the size of a household is not commonly taken into account in such measures may distort any analysis of fluctuations within or among the household income categories, and may render straight comparisons between quintiles hard or even incommunicable.[ten] The US Demography does non include noncash benefits such as wellness benefits.[11]
Recent trends [edit]
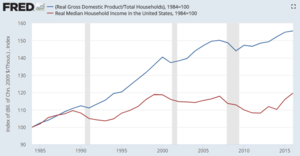
U.S. economical growth is not translating into higher median family incomes. Real Gdp per household has typically increased since the year 2000, while existent median income per household was beneath 1999 levels until 2016, indicating a trend of greater income inequality.[12]

Total bounty's share of GDP has declined by 4.5 percent points from 1970 to 2016. This implies that the share attributed to uppercase increased in that period.
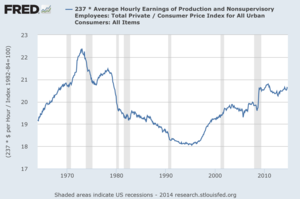
U.S. real wages (i.e. production) for ordinary (i.e. non-supervisory) workers remain slightly below their 1970s peak.[13]
The Current Population Survey of the U.Southward. Census Bureau reported in September 2017 that real median household income was $59,039 in 2016, exceeding any previous twelvemonth. This was the fourth sequent yr with a statistically significant increase by their measure.[14]
Changes in median income reverberate several trends: the aging of the population, irresolute patterns in work and schooling, and the evolving makeup of the American family, equally well equally long- and curt-term trends in the economic system itself. For case, the retirement of the Baby Boom generation should push button down overall median income, as more than persons enter lower-income retirement. Nevertheless, assay of different working age groups indicate a like pattern of stagnating median income too.[15]
Journalist Annie Lowrey wrote in September 2014: "The root causes [of wage stagnation] include technological alter, the decline of labor unions, and globalization, economists call back, though they disagree sharply on how much to weight each cistron. Merely foreign-produced appurtenances became sharply cheaper, pregnant imports climbed and product moved overseas. And computers took over for humans in many manufacturing, clerical, and administrative tasks, eroding middle-class jobs growth and suppressing wages."[16]
Some other line of analysis, known equally "full compensation," presents a more complete motion-picture show of existent wages. The Kaiser Family unit Foundation conducted a written report in 2013 which shows that employer contributions to employee healthcare costs went up 78% from 2003 to 2013.[17] The marketplace has made a trade-off: expanding benefits packages vs. increasing wages.
Measured relative to GDP, total bounty and its component wages and salaries have been declining since 1970. This indicates a shift in income from labor (persons who derive income from hourly wages and salaries) to uppercase (persons who derive income via ownership of businesses, land and assets). This trend is common across the developed globe, due in part to globalization.[18] Wages and salaries have fallen from approximately 51% Gdp in 1970 to 43% Gross domestic product in 2013. Total bounty has fallen from approximately 58% GDP in 1970 to 53% GDP in 2013.[19]
Still, every bit indicated by the charts beneath, household income has still increased significantly since the tardily 1970s and early 80s in real terms, partly due to higher private median wages, and partly due to increased employment of women.
According to the CBO, betwixt 1979 and 2011, gross median household income, adjusted for inflation, rose from $59,400 to $75,200, or 26.five%.[xx] However, in one case adjusted for household size and looking at taxes from an after-tax perspective, real median household income grew 46%, representing significant growth.[21]
The post-obit table summarizes real median household income at fundamental recent milestones:
| Variable | 1999 Previous Record | 2007 Pre-Crunch Peak | 2012 Post-Crunch Trough | 2016 Previous Record | 2017 Previous Record | 2018 Tape |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Real median household income[22] | $61,526 | $threescore,985 | $55,900 | $61,779 | $62,626 | $63,179 |
Uses [edit]
Use of individual household income: The authorities and organizations may look at one particular household's income to decide if a person is eligible for certain programs, such as nutrition help [23] or need-based financial aid,[24] among many others.
Use at the aggregate level: Summaries of household incomes across groups of people – oft the unabridged country – are also studied equally role of economical trends like standard of living and distribution of income and wealth. Household income equally an economical measure can exist represented as a median, a mean, a distribution, and other means. Household income can be studied across time, region, didactics level, race/ethnicity, and many other dimensions. As an indicator of economic trends, it may be studied along with related economic measures such equally disposable income, debt, household cyberspace worth (which includes debt and investments, durable goods like cars and houses), wealth, and employment statistics.
Median inflation-adjusted ("existent") household income [edit]
Median inflation-adjusted ("existent") household income generally increases and decreases with the business organization bike, declining in each year during the periods 1979 through 1983, 1990 through 1993, 2000 through 2004 and 2008 through 2012, while rising in each of the intervening years.[20] Farthermost poverty in the United States, meaning households living on less than $2 per person per twenty-four hour period earlier regime benefits, more than than doubled in absolute terms from 636,000 to 1.46 1000000 households (including 2.8 million children) between 1996 and 2011, with nigh of this increase occurring between late 2008 and early on 2011.[25]

Median household income, by county, equally of 2017.
CBO income growth report [edit]
The nonpartisan Congressional Upkeep Office conducted a study analyzing household income throughout the income distribution, by combining the Census and IRS income information sources. Unlike the Demography measure of household income, the CBO showed income before and afterward taxes, and past besides taking into account household size.[26] Too, the CBO definition of income is much broader, and includes in kind transfers as well as all monetary transfers from the regime.[26] The Census' official definition of money income excludes food stamps and the EITC, for example, while CBO includes it.
Betwixt 1979 and 2011, gross median household income, adjusted for inflation, rose from $59,400 to $75,200, or 26.5%. This compares with the Census' growth of ten%.[twenty] Withal, once adjusted for household size and looking at taxes from an after-tax perspective, real median household income grew 46%, representing significant growth.[21]
While median gross household income showed much stronger growth than depicted by the Census, inequality was shown to still have increased. The top 10% saw gross household income abound past 78%, versus 26.5% for the median. The bottom 10%, using the same measure, saw college growth than the median (40%).[21]
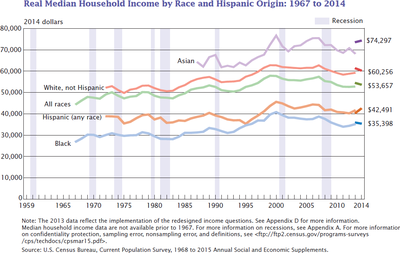
This graph shows the income since 1970 of different racial and indigenous groups in the U.s.a. (in 2014 dollars).[27]
Since 1980, U.Southward. gdp (Gdp) per capita has increased 67%,[28] while median household income has but increased by 15%. Median household income is a politically sensitive indicator. Voters can exist disquisitional of their regime if they perceive that their cost of living is ascension faster than their income.
The early-2000s recession began with the bursting of the dot-com bubble and affected near advanced economies including the European Matrimony, Japan and the United States. An economical recession will normally cause household incomes to decrease, often by as much every bit 10%.
The tardily-2000s recession began with the bursting of the U.S. housing bubble, which caused a problem in the dangerously exposed sub prime-mortgage market. This in turn triggered a global financial crisis. In constant price, 2011 American median household income was ane.13% lower than what information technology was in 1989. This corresponds to a 0.05% annual subtract over a 22-year flow.[29] In the meantime, Gross domestic product per capita has increased past 33.8% or 1.33% annually.[30]
A written report on United states Census income data claims that when using the national bookkeeping methodology, U.Due south. gross median household income was $57,739 in 2010 (table 3).[31]
In 2015, the U.s. median household income spiked 5.two per cent, reaching $56,000, making information technology the first annual hike in median household income since the offset of the Great Recession.[32]
Mean household income [edit]
Another common measurement of personal income is the mean household income. Unlike the median household income, which divides all households in two halves, the mean income is the average income earned past American households. In the case of hateful income, the income of all households is divided by the number of all households.[33] The hateful income is more than affected by the relatively unequal distribution of income which tilts towards the top.[34] Equally a event, the hateful will exist higher than the median income, with the tiptop earning households boosting it. Overall, the mean household income in the United States, according to the U.s. Census Bureau 2014 Annual Social and Economic Supplement, was $72,641.[35]
The The states Census Bureau also provides a breakup by self-identified ethnic groups as follows (as of March 2018):
| Indigenous category | Mean household income |
|---|---|
| Asian solitary | $112,105 |
| White alone | $99,632 |
| Hispanic or Latino | $threescore,319 |
| Black | $63,985 |
Mean vs. median household income [edit]
Median income is the corporeality which divides the income distribution into two equal groups, half having income above that corporeality, and half having income beneath that amount. Hateful income (average) is the corporeality obtained past dividing the total aggregate income of a group by the number of units in that grouping. The means and medians for households and families are based on all households and families. Means and medians for people are based on people 15 years sometime and over with income.
—US Census Bureau, Frequently Asked Question, published past Offset Gov.[33]
Aggregate income distribution [edit]
| | This section needs to be updated. (August 2018) |
The aggregate income measures the combined income earned by all persons in a particular income grouping. In 2018, the total personal income earned in the United States was $17.six trillion.[36] In 2008, all households in the U.s. earned roughly $12,442.2 billion.[36] One one-half, 49.98%, of all income in the US was earned by households with an income over $100,000, the top twenty pct. Over i quarter, 28.5%, of all income was earned by the top 8%, those households earning more than $150,000 a year. The top 3.65%, with incomes over $200,000, earned 17.five%. Households with almanac incomes from $50,000 to $75,000, xviii.2% of households, earned 16.5% of all income. Households with annual incomes from $50,000 to $95,000, 28.i% of households, earned 28.8% of all income. The bottom 10.3% earned 1.06% of all income.[ citation needed ]
Household income and demographics [edit]
Racial and ethnic groups [edit]

in 2005
White Americans made upwards roughly 75.1% of all people in 2000,[37] 87.93% of all households in the elevation 5% were headed by a person who identified every bit beingness White solitary. Just four.75% of all household in the top 5% were headed by someone who identified every bit Hispanic or Latino of whatsoever race,[38] versus 12.5% of persons identifying themselves equally Hispanic or Latino in the general population.[37]
Overall, 86.01% of all households in the top two quintiles with upper-eye range incomes of over $55,332 were headed past someone identifying as White alone, while vii.21% were being headed by someone who identified as Hispanic and 7.37% by someone who identified as African American or Black.[38] Overall, households headed by Hispanics and African Americans were underrepresented in the elevation two quintiles and overrepresented in the bottom two quintiles. Households headed by people who identified as being Asian alone were also overrepresented among the tiptop 2 quintiles. In the top five percentage the percentage of Asians was most twice every bit high as the percentage of Asians amongst the full general population. Whites were relatively even distributed throughout the quintiles only being underrepresented in the lowest quintile and slightly overrepresented in the top quintile and the pinnacle five pct.[38]
In terms of race in 2004 information, Asian-American households had the highest median household income of $57,518, European-American households ranked second with $48,977, Hispanic or Latino households ranked third with $34,241. African-American or Black households had the lowest median household income of all races with $thirty,134.[39]
| Indigenous group | All households | Lowest fifth | Second 5th | Eye 5th | Fourth 5th | Highest fifth | Top 5% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White alone | Number in 1000s | 92,702 | 16,940 | 18,424 | 18,978 | 19,215 | xix,721 | 5,029 |
| Per centum | 81.93% | 74.87% | 81.42% | 83.87% | 84.92% | 87.16% | 87.93% | |
| Asian lone | Number in 1000s | four,140 | 624 | 593 | 786 | 871 | 1,265 | 366 |
| Per centum | 3.65% | two.76% | two.26% | 3.47% | 3.84% | 5.59% | 6.46% | |
| Blackness | Number in 1000s | xiii,792 | 4,474 | iii,339 | 2,637 | 2,053 | one,287 | 236 |
| Pct | 12.nineteen% | nineteen.77% | xiv.75% | eleven.65% | 9.07% | 5.69% | 4.17% | |
| Hispanic or Latino (of whatever race) | Number in 1000s | 12,838 | 3,023 | 3,130 | 2,863 | 1,931 | 1,204 | 269 |
| Per centum | eleven.33% | thirteen.56% | thirteen.83% | 12.20% | 8.53% | 5.89% | 4.75% | |
Source: US Census Bureau, 2004 [38]
Education and gender [edit]
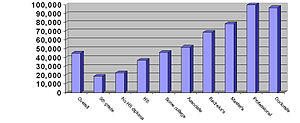
Median annual household income in accord with the householder's educational attainment. The data only includes households with a householder over the age of 20-five.[40]
Household income every bit well as per capita income in the United states of america rise significantly equally the educational attainment increases.[41] In 2005 graduates with a Main'due south in Business concern Administration (MBA) who accepted job offers were expected to earn a base bacon of $88,626. They were also expected to receive an "average signing bonus of $17,428."[42]
According to the United states of america Census Agency persons with doctorates in the United States had an average income of roughly $81,400. The average for an advanced degree was $72,824, with men averaging $90,761 and women averaging $50,756 annually. Twelvemonth-circular total-fourth dimension workers with a professional degree had an boilerplate income of $109,600 while those with a master's degree had an boilerplate income of $62,300. Overall, "…[a]verage earnings ranged from $18,900 for high school dropouts to $25,900 for loftier school graduates, $45,400 for higher graduates and $99,300 for workers with professional degrees (M.D., O.D., D.P.T., D.P.M., D.O., J.D., Pharm.D., D.D.Due south., or D.V.M.)."[43]
Individuals with graduate degrees have an average per capita income exceeding the median household income of married couple families amongst the general population ($63,813 annually).[43] [44] College educational attainment did not, still, help close the income gap between the genders as the life-time earnings for a male with a professional degree were roughly forty pct (39.59%) college than those of a female person with a professional degree. The lifetime earnings gap between males and females was the smallest for those individuals holding an associate degrees with male life-fourth dimension earnings being 27.77% higher than those of females. While educational attainment did not help reduce the income inequality between men and women, it did increase the earnings potential of individuals of both sexes, enabling many households with 1 or more graduate degree householders to enter the height household income quintile.[43] These data were not adjusted for preferential differences among men and women whom attend college.
Household income as well increased significantly with the educational attainment of the householder. The US Census Bureau publishes educational attainment and income data for all households with a householder who was anile 20-five or older. The biggest income difference was between those with some higher didactics and those who had a Bachelor's caste, with the latter making $23,874 more annually. Income besides increased essentially with increased mail service-secondary education. While the median annual household income for a household with a householder having an acquaintance degree was $51,970, the median annual household income for householders with a bachelor'due south degree or higher was $73,446. Those with doctorates had the second highest median household with a median of $96,830; $18,289 more than that for those at the master's degree level, only $3,170 lower than the median for households with a professional caste holding householder.[forty]
| Criteria | Overall | Less than 9th grade | Some high school | High school graduate or equivalent | Some college | Associate degree | Bachelor's degree | Bachelor's degree or more than | Master's degree | Professional degree | Doctoral degree | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median annual individual income | Male, age 25+ | $33,517 | $fifteen,461 | $18,990 | $28,763 | $35,073 | $39,015 | $fifty,916 | $55,751 | $61,698 | $88,530 | $73,853 |
| Female, historic period 25+ | $19,679 | $9,296 | $10,786 | $15,962 | $21,007 | $24,808 | $31,309 | $35,125 | $41,334 | $48,536 | $53,003 | |
| Median annual household income[45] | $62,625 | $26,587 | $30,100 | $44,970 | $55,563 | $64,263 | $91,772 ? | $100,021 | $108,231 | $139,069 | $140,110 | |
The alter in median personal and household since 1991 as well varied greatly with educational attainment. The following tabular array shows the median household income according to the educational attainment of the householder. All data is in 2003 dollars and simply applies to householders whose householder is aged twenty-5 or older. The highest and lowest points of the median household income are presented in bold face.[40] [46] Since 2003, median income has continued to ascent for the nation as a whole, with the biggest gains going to those with acquaintance degrees, available'southward degree or more, and master's degrees. High-school dropouts fared worse with negative growth.
| Year | Overall Median | Less than ninth grade | Some loftier school | High school graduate | Some college | Associate degree | Available'south degree | Bachelor's degree or more | Master'due south degree | Professional degree | Doctoral degree |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1991 | $40,873 | $17,414 | $23,096 | $37,520 | $46,296 | $52,289 | $64,150 | $68,845 | $72,669 | $102,667 | $92,614 |
| 1993 | $40,324 | $17,450 | $22,523 | $35,979 | $44,153 | $49,622 | $64,537 | $70,349 | $75,645 | $109,900 | $93,712 |
| 1995 | $42,235 | $18,031 | $21,933 | $37,609 | $44,537 | $50,485 | $63,357 | $69,584 | $77,865 | $98,302 | $95,899 |
| 1997 | $43,648 | $17,762 | $22,688 | $38,607 | $45,734 | $51,726 | $67,487 | $72,338 | $77,850 | $105,409 | $99,699 |
| 1999 | $46,236 | $19,008 | $23,977 | $39,322 | $48,588 | $54,282 | $70,925 | $76,958 | $82,097 | $110,383 | $107,217 |
| 2001 | $42,900 | $xviii,830 | $24,162 | $37,468 | $47,605 | $53,166 | $69,796 | $75,116 | $81,993 | $103,918 | $96,442 |
| 2003 | $45,016 | $18,787 | $22,718 | $36,835 | $45,854 | $56,970 | $68,728 | $73,446 | $78,541 | $100,000 | $96,830 |
| Boilerplate | $43,376 | $eighteen,183 | $23,013 | $37,620 | $46,109 | $51,934 | $66,997 | $72,376 | $78,094 | $104,368 | $94,487 |
Source: The states Census Bureau, 2003 [twoscore]
Age of householder [edit]

Household income in the United States varies substantially with the age of the person who heads the household. Overall, the median household income increased with the historic period of householder until retirement age when household income started to decline.[48] The highest median household income was found among households headed by working babe-boomers.[48]
Households headed by persons between the ages of 45 and 54 had a median household income of $61,111 and a mean household income of $77,634. The median income per member of household for this detail grouping was $27,924. The highest median income per fellow member of household was among those between the ages of 54 and 64 with $30,544 [The reason this figure is lower than the next group is because pensions and Social Security add together to income while a portion of older individuals besides accept work-related income.].[48]
The group with the second highest median household income, were households headed past persons between the ages 35 and 44 with a median income of $56,785, followed past those in the age grouping between 55 and 64 with $50,400. Not surprisingly the lowest income group was composed of those households headed by individuals younger than 24, followed by those headed past persons over the age of 75. Overall, households headed by persons above the age of seventy-five had a median household income of $20,467 with the median household income per fellow member of household being $18,645. These figures support the full general assumption that median household income likewise equally the median income per member of household peaked among those households headed by centre aged persons, increasing with the age of the householder and the size of the household until the householder reaches the age of 64. With retirement income replacing salaries and the size of the household declining, the median household income decreases equally well.[48]
Household size [edit]
While median household income has a tendency to increase up to four persons per household, it declines for households beyond 4 persons. For case, in the country of Alabama in 2004, 2-person households had a median income of $39,755, with $48,957 for three-person households, $54,338 for iv-person households, $l,905 for 5-person households, $45,435 for six-person households, with seven-or-more-person households having the second everyman median income of just $42,471.[49]
Geography [edit]
Considering other racial and geographical differences in regards to household income, it should come as no surprise that the median household income varies with race, size of household and geography. The state with the highest median household income in the United States every bit of the United states of america Census Bureau 2009 is Maryland with $69,272, followed by New Bailiwick of jersey, Connecticut and Alaska, making the Northeastern United states of america the wealthiest area by income in the entire country.[50]
Regionally, in 2010, the Northeast reached a median income of $53,283, the West, $53,142, the South, $45,492, and the Midwest, $48,445.[51] Each effigy represents a decline from the previous year.
Median household income by country [edit]
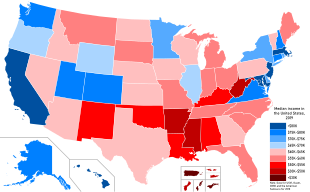
Map of states by median household income in 2019.
In 2007, the median household income by state ranged from $36,338 in Mississippi to $68,080 in Maryland. Despite having the highest median home price in the nation[52] and home prices that far outpaced incomes,[53] California ranked only 8th in income that year, with a median household income of $59,984. While California's median income was non nigh enough to afford the average California home or even a starter dwelling, West Virginia, which had one of the nation's everyman median household incomes, also had the nation's everyman median home price.[52] [54]
When grouped past Census Agency Region, of the 15 states that, in 2017, had the highest median household income, just Minnesota is located in the Mid-West. 5 are in the Northeast (Connecticut, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New Jersey and Rhode Island), three are S Atlantic states (Washington D.C., Maryland and Virginia) while the remaining six are in the West (Alaska, California, Colorado, Hawaii, Washington and Utah).
The southern states had, on average, the lowest median household income, with nine of the land'due south 15 poorest states located in the South. However, nigh of the poverty in the S is located in rural areas. Metropolitan areas such as Atlanta, Nashville, Charlotte, Raleigh, Birmingham, Dallas, Houston, and Miami are areas within the southern states that take above average income levels. Overall, median household income tended to be the highest in the nation'southward most urbanized northeastern, upper midwestern and west declension states, while rural areas, mostly in the southern and mountain states (like New Mexico, Montana and Idaho), had the lowest median household income.[54]
Equally of 2019, the median household income ranged from $20,474 in Puerto Rico to $92,266 in the District of Columbia. Notation that the U.Southward. Census Bureau treats Puerto Rico as if information technology were a state (Puerto Rico is included in the American Community Survey).[55]
All data is from the 2009–2019 American Community Survey i-Year Estimates.[56] [57] [58] [59] [60]
| Rank | +/- * | Land or territory | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | 2009 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | +8 | Commune of Columbia | $92,266 | $85,203 | $82,336 | $75,506 | $75,628 | $71,648 | $67,572 | $65,246 | $66,583 | $63,124 | $59,290 |
| ii | −1 | Maryland | $86,738 | $83,242 | $eighty,776 | $78,945 | $75,847 | $73,971 | $72,483 | $71,836 | $70,004 | $68,854 | $69,272 |
| 3 | +three | Massachusetts | $85,843 | $79,835 | $77,385 | $75,297 | $70,628 | $69,160 | $66,768 | $65,339 | $62,859 | $62,072 | $64,081 |
| 4 | −ii | New Jersey | $85,751 | $81,740 | $80,088 | $76,126 | $72,222 | $72,919 | $70,165 | $69,667 | $67,458 | $67,681 | $68,342 |
| 5 | - | Hawaii | $83,102 | $80,212 | $77,765 | $74,511 | $73,486 | $69,592 | $68,020 | $66,259 | $61,821 | $63,030 | $64,098 |
| half dozen | +iv | California | $lxxx,440 | $75,277 | $71,805 | $67,739 | $64,500 | $61,933 | $sixty,190 | $58,328 | $57,287 | $57,708 | $58,931 |
| 7 | −4 | Connecticut | $78,833 | $76,348 | $74,168 | $73,433 | $71,346 | $70,048 | $67,098 | $67,276 | $65,753 | $64,032 | $67,034 |
| 8 | +4 | Washington | $78,687 | $74,043 | $70,979 | $67,106 | $64,129 | $61,366 | $58,405 | $57,573 | $56,835 | $55,631 | $56,548 |
| 9 | −2 | New Hampshire | $77,933 | $74,991 | $73,381 | $70,936 | $70,303 | $66,532 | $64,230 | $63,280 | $62,647 | $61,042 | $lx,567 |
| 10 | +4 | Colorado | $77,127 | $71,953 | $69,117 | $65,685 | $63,909 | $61,303 | $58,823 | $56,765 | $55,387 | $54,046 | $55,430 |
| 11 | −3 | Virginia | $76,456 | $72,577 | $71,535 | $68,114 | $66,262 | $64,902 | $62,666 | $61,741 | $61,882 | $60,674 | $59,330 |
| 12 | +three | Utah | $75,780 | $71,414 | $68,358 | $65,977 | $62,912 | $60,922 | $59,770 | $57,049 | $55,869 | $54,744 | $55,117 |
| thirteen | −nine | Alaska | $75,463 | $74,346 | $73,181 | $76,440 | $73,355 | $71,583 | $72,237 | $67,712 | $67,825 | $64,576 | $66,953 |
| fourteen | −one | Minnesota | $74,593 | $lxx,315 | $68,388 | $65,599 | $63,488 | $61,481 | $sixty,702 | $58,906 | $56,954 | $55,459 | $55,616 |
| 15 | +1 | New York | $72,108 | $67,844 | $64,894 | $62,909 | $60,850 | $58,878 | $57,369 | $56,448 | $55,246 | $54,148 | $54,659 |
| 16 | +1 | Rhode Isle | $71,169 | $64,340 | $63,870 | $60,596 | $58,073 | $54,891 | $55,902 | $54,554 | $53,636 | $52,254 | $54,119 |
| 17 | −6 | Delaware | $70,176 | $64,805 | $62,852 | $61,757 | $61,255 | $59,716 | $57,846 | $54,554 | $58,814 | $55,847 | $56,860 |
| 18 | - | Illinois | $69,187 | $65,030 | $62,992 | $sixty,960 | $59,588 | $57,444 | $56,210 | $55,137 | $53,234 | $52,972 | $53,966 |
| 19 | +6 | Oregon | $67,058 | $63,246 | $threescore,212 | $57,532 | $54,148 | $51,075 | $50,251 | $49,161 | $46,816 | $46,560 | $48,457 |
| xx | - | Wyoming | $65,003 | $61,584 | $60,434 | $59,882 | $60,214 | $57,055 | $58,752 | $54,901 | $56,322 | $53,512 | $52,664 |
| 21 | +8 | N Dakota | $64,577 | $63,837 | $61,843 | $60,656 | $60,557 | $59,029 | $55,759 | $53,585 | $51,704 | $48,670 | $47,827 |
| 22 | - | Wisconsin | $64,168 | $60,773 | $59,305 | $56,811 | $55,638 | $52,622 | $51,467 | $51,059 | $l,395 | $49,001 | $49,993 |
| 23 | +4 | Texas | $64,034 | $threescore,629 | $59,206 | $56,565 | $55,653 | $53,035 | $51,704 | $50,740 | $49,392 | $48,615 | $48,259 |
| 24 | –1 | Pennsylvania | $63,463 | $60,905 | $59,195 | $56,907 | $55,702 | $53,234 | $52,007 | $51,230 | $fifty,228 | $49,288 | $49,520 |
| 25 | −6 | Nevada | $63,276 | $58,646 | $58,003 | $55,180 | $52,431 | $51,450 | $51,230 | $49,760 | $48,927 | $51,001 | $53,341 |
| 26 | - | Nebraska | $63,229 | $59,566 | $59,970 | $56,927 | $54,996 | $52,686 | $51,440 | $50,723 | $l,296 | $52,504 | $48,408 |
| 27 | −half dozen | Vermont | $63,001 | $60,782 | $57,513 | $57,677 | $56,990 | $54,166 | $52,578 | $52,997 | $52,776 | $49,406 | $51,618 |
| 28 | +2 | Kansas | $62,087 | $58,218 | $56,422 | $54,935 | $53,906 | $52,504 | $l,972 | $50,241 | $48,264 | $48,257 | $47,817 |
| 29 | −5 | Arizona | $62,055 | $59,246 | $56,581 | $53,558 | $51,492 | $50,068 | $48,510 | $47,826 | $46,709 | $46,789 | $48,745 |
| 30 | +eight | Georgia | $61,980 | $58,756 | $56,183 | $53,559 | $51,244 | $49,321 | $47,829 | $47,209 | $46,007 | $46,430 | $44,736 |
| 31 | −3 | Iowa | $61,691 | $59,955 | $58,570 | $56,247 | $54,736 | $53,712 | $52,229 | $50,957 | $49,427 | $47,961 | $48,044 |
| 32 | +5 | Idaho | $lx,999 | $55,583 | $52,225 | $51,807 | $48,275 | $47,861 | $46,783 | $45,489 | $43,341 | $43,490 | $44,926 |
| 33 | +1 | Michigan | $59,584 | $56,697 | $54,909 | $52,492 | $51,084 | $49,847 | $48,273 | $46,859 | $45,981 | $45,413 | $45,255 |
| 34 | +2 | South Dakota | $59,533 | $56,274 | $56,894 | $54,467 | $53,017 | $50,979 | $48,947 | $48,362 | $48,321 | $45,904 | $45,043 |
| 35 | +4 | Florida | $59,227 | $55,462 | $52,594 | $50,860 | $49,426 | $47,463 | $46,036 | $45,040 | $44,299 | $44,409 | $44,736 |
| 36 | −5 | Maine | $58,924 | $55,602 | $56,277 | $53,079 | $51,494 | $49,462 | $46,974 | $46,709 | $46,033 | $45,815 | $45,734 |
| 37 | −4 | Ohio | $58,642 | $56,111 | $54,021 | $52,334 | $51,075 | $49,308 | $48,081 | $46,829 | $45,749 | $45,090 | $45,395 |
| 38 | −6 | Indiana | $57,603 | $55,746 | $54,181 | $52,314 | $l,532 | $49,446 | $47,529 | $46,974 | $46,438 | $44,613 | $45,424 |
| 39 | −4 | Missouri | $57,409 | $54,478 | $53,578 | $51,746 | $l,238 | $48,363 | $46,931 | $45,321 | $45,247 | $44,301 | $45,229 |
| 40 | - | North Carolina | $57,341 | $53,855 | $52,752 | $50,584 | $47,830 | $46,556 | $45,906 | $45,150 | $43,916 | $43,326 | $43,674 |
| 41 | +3 | Montana | $57,153 | $55,328 | $53,386 | $fifty,027 | $49,509 | $46,328 | $46,972 | $45,076 | $44,222 | $42,666 | $42,322 |
| 42 | - | South Carolina | $56,227 | $52,306 | $l,570 | $49,501 | $47,238 | $45,238 | $44,163 | $43,107 | $43,916 | $42,018 | $42,442 |
| 43 | +ii | Tennessee | $56,071 | $52,375 | $51,340 | $48,547 | $47,275 | $44,361 | $44,297 | $42,764 | $41,693 | $41,461 | $41,725 |
| 44 | +two | Oklahoma | $54,449 | $51,924 | $50,051 | $49,176 | $48,568 | $47,529 | $45,690 | $44,312 | $43,225 | $42,072 | $41,664 |
| 45 | +iii | Kentucky | $52,295 | $fifty,247 | $48,375 | $46,659 | $44,765 | $42,958 | $43,399 | $41,724 | $41,141 | $twoscore,062 | $40,072 |
| 46 | −five | New Mexico | $51,945 | $47,169 | $46,744 | $46,748 | $45,382 | $44,803 | $43,872 | $42,558 | $41,963 | $42,090 | $43,028 |
| 47 | - | Alabama | $51,734 | $49,861 | $48,123 | $46,257 | $44,765 | $42,830 | $42,849 | $41,574 | $41,415 | $forty,474 | $40,489 |
| 48 | −5 | Louisiana | $51,073 | $47,905 | $46,145 | $45,146 | $45,727 | $44,555 | $44,164 | $42,944 | $41,734 | $42,505 | $42,429 |
| 49 | +2 | Arkansas | $48,952 | $47,062 | $45,869 | $45,907 | $42,798 | $44,922 | $39,376 | $39,018 | $41,302 | $38,587 | $36,538 |
| 50 | −1 | West Virginia | $48,850 | $44,097 | $43,469 | $43,385 | $42,019 | $41,059 | $41,253 | $40,196 | $38,482 | $37,218 | $37,435 |
| 51 | −i | Mississippi | $45,792 | $44,717 | $43,529 | $41,754 | $40,593 | $39,680 | $37,963 | $37,095 | $36,919 | $36,851 | $36,646 |
| 52 | — | Puerto Rico | $xx,474 | $twenty,296 | $19,775 | $xx,078 | $18,810 | $xviii,948 | $19,183 | $nineteen,630 | — | — | — |
*change since 2009
The median personal income per person, after adjusting for costs of living with local regional price parities and the national PCE price index, averaged $47,807 in 2016 (in 2012 chained dollars). Median adjusted personal income per capita varied from $39,901 in Mississippi to $61,601 in Connecticut (and $64,363 in the District of Columbia). U.s.a. closest to the national average were California and Vermont, at $48,384 and $47,971 respectively.[61]
Median household income by U.South. territory [edit]
Below is the median household income for the U.S. territories in 2010 (for four of the five inhabited territories).[62] Note that Puerto Rico is not included in this table, and is instead included in the table above (because Puerto Rico is included in the ACS, as if information technology were a land).
| Rank | Territory | 2010 U.Due south. Demography |
|---|---|---|
| i | Guam | $48,274 |
| two | U.S. Virgin Islands | $37,254 |
| 3 | American Samoa | $23,892 |
| iv | Northern Mariana Islands | $19,958 |
[edit]
Household income is one of the most usually used measures of income and, therefore, too one of the nearly prominent indicators of social class. Household income and instruction practise not, even so, always reflect perceived class status correctly. Sociologist Dennis Gilbert acknowledges that "... the class structure... does not exactly match the distribution of household income" with "the mismatch [existence] greatest in the centre..." (Gilbert, 1998: 92) As social classes commonly overlap, it is not possible to define exact class boundaries.
Co-ordinate to Leonard Beeghley[ citation needed ] a household income of roughly $95,000 would be typical of a dual-earner center class household while $lx,000 would be typical of a dual-earner working class household and $18,000 typical for an impoverished household. William Thompson and Joseph Hickey[ commendation needed ] see mutual incomes for the upper course as those exceeding $500,000 with upper middle class incomes ranging from the high five-figures to well-nigh commonly in excess of $100,000. They claim the lower middle class ranges from $35,000 to $75,000; $16,000 to $thirty,000 for the working course and less than $two,000 for the lower class.
| Dennis Gilbert, 2002 | William Thompson & Joseph Hickey, 2005 | Leonard Beeghley, 2004 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Typical characteristics | Class | Typical characteristics | Class | Typical characteristics |
| Capitalist class (1%) | Peak-level executives, high-rung politicians, heirs. Ivy League education mutual. | Upper class (1%) | Superlative-level executives, celebrities, heirs; income of $500,000+ common. Ivy league educational activity common. | The super-rich (0.9%) | Multi-millionaires whose incomes commonly exceed $three.5 million or more than; includes celebrities and powerful executives/politicians. Ivy League educational activity mutual. |
| Upper heart class[1] (15%) | Highly-educated (often with graduate degrees), almost ordinarily salaried, professionals and middle management with big work autonomy. | Upper middle class[1] (15%) | Highly-educated (often with graduate degrees) professionals & managers with household incomes varying from the high v-figure range to ordinarily above $100,000. | The rich (5%) | Households with net worth of $1 million or more; largely in the grade of abode equity. Generally have college degrees. |
| Eye course (plurality/ bulk?; ca. 46%) | College-educated workers with considerably higher-than-average incomes and bounty; a homo making $57,000 and a adult female making $40,000 may be typical. | ||||
| Lower middle class (30%) | Semi-professionals and craftsmen with a roughly boilerplate standard of living. Most accept some college education and are white-collar. | Lower middle class (32%) | Semi-professionals and craftsmen with some work autonomy; household incomes unremarkably range from $35,000 to $75,000. Typically, some college education. | ||
| Working course (30%) | Clerical and well-nigh blueish-neckband workers whose work is highly routinized. Standard of living varies depending on number of income earners, but is commonly simply acceptable. High school education. | ||||
| Working course (32%) | Clerical, pink- and bluish-neckband workers with often low job security; mutual household incomes range from $sixteen,000 to $30,000. Loftier school education. | Working form (ca. twoscore–45%) | Blue-collar workers and those whose jobs are highly routinized with low economic security; a man making $40,000 and a woman making $26,000 may be typical. High school instruction. | ||
| Working poor (13%) | Service, low-rung clerical and some blue-collar workers. Loftier economic insecurity and gamble of poverty. Some high school instruction. | ||||
| Lower class (ca. 14–twenty%) | Those who occupy poorly-paid positions or rely on government transfers. Some high school education. | ||||
| Underclass (12%) | Those with limited or no participation in the labor force. Reliant on regime transfers. Some high school didactics. | The poor (ca. 12%) | Those living below the poverty line with limited to no participation in the labor force; a household income of $18,000 may be typical. Some high school education. | ||
| |||||
Distribution of household income [edit]
Distribution of household income in 2014 according to United states of america Census data [edit]

Percentage of persons and households in each of the income groups shown.[ citation needed ]

The pct of households with half-dozen effigy incomes and individuals with incomes in the elevation 10%, exceeding $77,500.[ commendation needed ]
| Income of Household | Number (thousands) [63] | Pct | Percentile | Hateful Income [63] | Mean number of earners [64] | Mean size of household [64] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 124,587 | — | — | $75,738 | ane.28 | 2.54 |
| Under $5,000 | 4571 | 3.67% | 0 | $1,080 | 0.20 | 1.91 |
| $5,000 to $9,999 | 4320 | iii.47% | iii.67th | $seven,936 | 0.34 | one.78 |
| $10,000 to $14,999 | 6766 | five.43% | 7.14th | $12,317 | 0.39 | 1.71 |
| $15,000 to $xix,999 | 6779 | 5.44% | 12.57th | $17,338 | 0.54 | 1.ninety |
| $twenty,000 to $24,999 | 6865 | v.51% | 18.01th | $22,162 | 0.73 | ii.07 |
| $25,000 to $29,999 | 6363 | five.xi% | 23.52th | $27,101 | 0.82 | 2.19 |
| $30,000 to $34,999 | 6232 | five.00% | 28.63th | $32,058 | 0.94 | 2.27 |
| $35,000 to $39,999 | 5857 | four.70% | 33.63th | $37,061 | 1.04 | 2.31 |
| $forty,000 to $44,999 | 5430 | 4.36% | 38.33th | $41,979 | 1.xv | 2.xl |
| $45,000 to $49,999 | 5060 | iv.06% | 42.69th | $47,207 | 1.24 | two.52 |
| $fifty,000 to $54,999 | 5084 | 4.08% | 46.75th | $51,986 | 1.32 | two.54 |
| $55,000 to $59,999 | 4220 | 3.39% | 50.83th | $57,065 | 1.41 | two.56 |
| $60,000 to $64,999 | 4477 | 3.59% | 54.22th | $62,016 | 1.46 | 2.64 |
| $65,000 to $69,999 | 3709 | 2.98% | 57.81st | $67,081 | 1.51 | ii.67 |
| $lxx,000 to $74,999 | 3737 | three.00% | 60.79th | $72,050 | ane.57 | ii.73 |
| $75,000 to $79,999 | 3484 | 2.eighty% | 63.79th | $77,023 | 1.60 | two.79 |
| $80,000 to $84,999 | 3142 | 2.52% | 66.58th | $81,966 | 1.63 | 2.79 |
| $85,000 to $89,999 | 2750 | 2.21% | 69.11th | $87,101 | one.77 | 2.90 |
| $90,000 to $94,999 | 2665 | 2.fourteen% | 71.31th | $92,033 | ane.82 | 2.96 |
| $95,000 to $99,999 | 2339 | 1.88% | 73.45th | $97,161 | one.81 | 2.97 |
| $100,000 to $104,999 | 2679 | 2.15% | 75.33th | $101,921 | ane.79 | 3.01 |
| $105,000 to $109,999 | 2070 | 1.66% | 77.48th | $107,187 | 1.88 | 3.01 |
| $110,000 to $114,999 | 1922 | 1.54% | 79.14th | $112,069 | 1.93 | 3.12 |
| $115,000 to $119,999 | 1623 | ane.30% | 80.68th | $117,133 | 1.98 | 3.14 |
| $120,000 to $124,999 | 1863 | 1.l% | 81.99th | $122,127 | 1.93 | three.09 |
| $125,000 to $129,999 | 1452 | 1.17% | 83.48th | $127,166 | 1.99 | three.12 |
| $130,000 to $134,999 | 1512 | one.21% | 84.65th | $131,863 | ii.00 | 3.18 |
| $135,000 to $139,999 | 1219 | 0.98% | 85.86th | $137,284 | 1.98 | 3.11 |
| $140,000 to $144,999 | 1290 | i.04% | 86.84th | $142,199 | 1.97 | 3.03 |
| $145,000 to $149,999 | 1024 | 0.82% | 87.87th | $147,130 | 2.01 | three.11 |
| $150,000 to $154,999 | 1146 | 0.92% | 88.70th | $151,940 | 1.85 | 3.12 |
| $155,000 to $159,999 | 848 | 0.68% | 89.62th | $157,177 | ii.08 | 3.15 |
| $160,000 to $164,999 | 875 | 0.seventy% | 90.30th | $162,019 | 2.02 | 3.xiii |
| $165,000 to $169,999 | 786 | 0.63% | 91.00th | $167,101 | 2.ten | iii.16 |
| $170,000 to $174,999 | 717 | 0.58% | 91.63th | $172,169 | ii.17 | three.21 |
| $175,000 to $179,999 | 607 | 0.49% | 92.21th | $177,187 | 2.19 | 3.28 |
| $180,000 to $184,999 | 619 | 0.fifty% | 92.69th | $182,055 | 2.03 | 3.xix |
| $185,000 to $189,999 | 556 | 0.45% | 93.19th | $187,299 | 2.03 | three.20 |
| $190,000 to $194,999 | 485 | 0.39% | 93.64th | $192,241 | 2.19 | 3.29 |
| $195,000 to $199,999 | 436 | 0.35% | 94.03th | $197,211 | 2.23 | 3.27 |
| $200,000 to $249,999 | 3249 | 2.61% | 94.38th | $220,267 | two.08 | 3.24 |
| $250,000 and over | 3757 | 3.02% | 96.98th | $402,476 |
Run across also [edit]
- List of countries by boilerplate wage
- Income inequality in the United States
- Economy of the U.s.
- Personal income in the The states
- Employee compensation in the United States
- Standard of living in the United States
General:
- Income inequality metrics
- Atkinson alphabetize
- Gini coefficient
- Hoover index
- Theil index
- International Ranking of Household Income
- Marriage gap
- Median income per household member
References [edit]
- ^ Federal Reserve Economical Data-Real Median Household Income-Retrieved September 15, 2018
- ^ a b "Income and Poverty in the U.s.: 2018" (PDF). census.gov. U.S. Department of Commerce. Retrieved July 20, 2020.
- ^ a b "Household Income: 2018" (PDF). demography.gov. U.S. Section of Commerce. Retrieved July 20, 2020.
- ^ "Existent Median Household Income in the United States.: 2018". stlouisfed.org . Retrieved October iii, 2019.
- ^ "Emmanuel Saez-Income and Wealth Inequality-Oct 2014" (PDF). Eml.berkeley.edu . Retrieved October xiv, 2017.
- ^ Tcherneva, Pavlina R. (August 2014). "This Chart Shows Just How (Un)Equal Things Are During A 'Champion' Of The 99%'s Administration". Contained Journal Review. Archived from the original on September thirteen, 2014. Retrieved September xiii, 2014.
- ^ Binyamin, Appelbaum (September four, 2014). "Fed Says Growth Lifts the Affluent, Leaving Behind Anybody Else". The New York Times . Retrieved September thirteen, 2014.
- ^ "Demography Long Course Definition". Usa Department of Housing and Urban Development. July thirty, 2009. Archived from the original on October 8, 2012.
- ^ "Glossary: household income". South Carolina Community Profiles. Archived from the original on April 21, 2006. Retrieved Baronial ten, 2006.
- ^ Gilbert, Dennis (1998). The American Grade Construction . New York: Wadsworth Publishing. ISBN0-534-50520-1.
- ^ "Near Income". United states of america Demography Agency. United States Census Bureau. Retrieved Apr 17, 2019.
- ^ Neil Irwin (September 17, 2014). "Y'all Can't Feed a Family With G.D.P." The New York Times.
- ^ Paul Krugman (Nov 12, 2014). "On Income Stagnation". The New York Times.
- ^ "U.S. Household Incomes Rose to Record in 2016 equally Poverty Fell". Bloomberg.com. September 12, 2017. Retrieved Oct 14, 2017.
- ^ "The American Eye Class Hasn't Gotten a Raise in 15 Years". Five Xxx Eight. September 22, 2014. Retrieved September 29, 2014.
- ^ Annie Lowrey. "Will Us Economy Always Be As Good As in the '90s?". Daily Intelligencer.
- ^ "2013 Summary of Findings – The Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation". Kff.org . Retrieved October 14, 2017.
- ^ "Monetary policy and long-term trends". Voxeu.org . Retrieved Oct 14, 2017.
- ^ "FRED Graph". Research.stlouisfed.org . Retrieved October 14, 2017.
- ^ a b c "Historical Income Tables – Households – U.South Census Bureau". Census.gov . Retrieved October fourteen, 2017.
- ^ a b c "The Distribution of Household Income and Federal Taxes, 2011". Cbo.gov . Retrieved October fourteen, 2017.
- ^ FRED-Real Median Household Income-Retrieved Apr 20, 2019
- ^ "WIC Income Eligibility Guidelines". United States Section of Agriculture. September 12, 2013. Archived from the original on September 13, 2014. Retrieved September 13, 2014.
- ^ "Federal Educatee Assist". U.S. Department of Instruction. September 12, 2013.
- ^ Shaefer, H. Luke; Edin, Kathryn (February 2012). "Farthermost Poverty in the United States, 1996 to 2011" (PDF). Policy Brief. National Poverty Centre (28).
- ^ a b "The Distribution of Household Income and Federal Taxes, 2011" (PDF). Congressional Budget Function.
- ^ DeNavas-Walt, Carmen; Proctor, Bernadette D.; Smith, Jessica C. (September 2012). "Real Median Household Income by Race and Hispanic Origin: 1967 to 2010". Income, Poverty, and Health Insurance Coverage in the United states: 2014 (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. p. 8.
- ^ "Report for Selected Countries and Subjects". www.international monetary fund.org.
- ^ "Income Data".
- ^ "Bureau of Economic Analysis". www.bea.gov.
- ^ "Archived re-create" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on Apr xi, 2015. Retrieved July 21, 2019.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ Picchi, Aimee (September xiii, 2016). "Median Household income increases". CBS News . Retrieved September 13, 2016.
- ^ a b "U.S. Census Bureau FAQs: What is the difference betwixt a median and a hateful?". United states of america Census Bureau. Archived from the original on September 22, 2006. Retrieved June 29, 2006.
- ^ "US Census Bureau on the nature the median in determining wealth" (PDF). May 2003. Retrieved June 29, 2006.
- ^ a b "Race and Hispanic Origin of Householder-Households by Median and Hateful Income". The states Demography Bureau. March 2018. Retrieved March 25, 2019.
- ^ a b "Personal income". U.Due south. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Archived from the original on January 24, 2020. Retrieved January 24, 2019.
- ^ a b "US Census Agency, 2000 Census racial data". Archived from the original on February 12, 2020. Retrieved June 29, 2006.
- ^ a b c d "U.s.a. Demography Bureau 2005 Economic survey, racial income distribution". Archived from the original on July 7, 2006. Retrieved June 29, 2006.
- ^ "US Demography Bureau, median household income according to certain demographic characteristics". August xxx, 2005. Archived from the original on June xviii, 2006. Retrieved June 29, 2006.
- ^ a b c d "Educational attainment and median household income". Archived from the original on September 3, 2006. Retrieved September 24, 2006.
- ^ "US Census Bureau, Income by education and sex". Archived from the original on April 11, 2006. Retrieved June 30, 2006.
- ^ "Wall Street Journal on MBA bacon base". 2006. Archived from the original on March xviii, 2007. Retrieved June 30, 2006.
- ^ a b c "United states Census Bureau on Education and Income" (PDF) . Retrieved June xxx, 2006.
- ^ "Infoplease, median household income". Infoplease.com . Retrieved June 29, 2006.
- ^ "Didactics Attainment of Householder-Households with Householder 25 Years Sometime or Over by Median and Mean Income, 1991–2017". Historical Income Tables. US Census Bureau. Retrieved March 26, 2019.
- ^ "Personal income and educational attainment, Usa Census Bureau". Archived from the original on September seven, 2006. Retrieved September 24, 2006.
- ^ Federal Reserve Bulletin. September 2017, Vol. 103, No. 3. See PDF: Changes in U.S. Family Finances from 2013 to 2016: Evidence from the Survey of Consumer Finances. Table 1 (on the left) is taken from page iv of the PDF. Table 2 (on the correct) is taken from page thirteen. See: Survey of Consumer Finances and more data.
- ^ a b c d "Usa Census Bureau median household income by historic period of householder". Archived from the original on May 28, 2006. Retrieved July seven, 2006.
- ^ "U.s.a. Census Agency, median family income past family unit size". Archived from the original on June 26, 2006. Retrieved June 29, 2006.
- ^ "US Census Agency, median household income by state". Archived from the original on June 28, 2006. Retrieved June 29, 2006.
- ^ DeNavas-Walt, Carmen; Proctor, Bernadette D.; Smith, Jessica C. (September 2011). Income, Poverty, and Health Insurance Coverage in the Us: 2010 (PDF). U.S. Demography Bureau. [ page needed ]
- ^ a b "Median habitation price by state". Clevelandfed.org. November 2005. Archived from the original on June 14, 2006. Retrieved July 1, 2006.
- ^ "The State of the Nation's Housing 2002" (PDF). Joint Eye for Housing Studies of Harvard Academy. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 10, 2011.
- ^ a b "US Census Bureau, median household income past state 2004". Archived from the original on June 28, 2006. Retrieved July one, 2006.
- ^ https://spider web.archive.org/web/20190830181655/http://www3.drcog.org/documents/archive/ACS_Basics.pdf U.S. Census Bureau. An Overview Of the American Community Survey. Folio 5 (archived). Retrieved July 2, 2020.
- ^ "Median income (dollars)—HOUSEHOLD INCOME Past RACE AND HISPANIC OR LATINO ORIGIN OF HOUSEHOLDER—Households—Guess in 52 Geos in 2019". Usa Census Bureau. Retrieved February 21, 2022.
- ^ https://www.census.gov/content/dam/Census/library/publications/2017/acs/acsbr16-02.pdf U.South. Census Bureau. Household Income: 2016. Retrieved July 2, 2020.
- ^ https://world wide web.census.gov/content/dam/Census/library/publications/2016/acs/acsbr15-02.pdf U.Due south. Census Bureau. Household Income: 2015. Retrieved July 2, 2020.
- ^ https://www2.census.gov/library/publications/2014/acs/acsbr13-02.pdf U.S. Demography Bureau. Household income: 2013. Retrieved July 2, 2020.
- ^ https://www.theweeklyjournal.com/politics/trump-signs-bill-avoiding-medicaid-cliff-for-puerto-rico-for/article_6905fce2-e473-11e9-9195-9fbdbb0490af.html Theweeklyjournal.com. Trump Signs Bill Avoiding Medicaid Cliff for Puerto Rico—For Now. Rosario Fajardo. October two, 2019. Retrieved July 2, 2020.
- ^ Bureau of Economic Analysis: Regional Data. RPI1 Real Personal Income per capita by state. U.Southward. Department of Commerce. Updated September 25, 2018. Retrieved Oct eight, 2018.
- ^ American FactFinder. U.South. Demography Agency. Profile of Selected Economic Characteristics: 2010. Tabular array DP-three (for American Samoa / Guam / Northern Mariana Islands / U.South. Virgin Islands). [URLs no longer bachelor]).
- ^ a b "Income Distribution to $250,000 or More for Households: 2014". Us Demography Bureau. Retrieved March 25, 2016.
- ^ a b "Selected Characteristics of Households, by Total Money Income in 2014" (XLS). U.s.a. Census Agency. Retrieved March 21, 2016. [ permanent dead link ]
External links [edit]
- Income, Poverty, and Health Insurance Coverage in the United States: 2003
- Reynolds, Alan (January viii, 2007). "Has U.Southward. Income Inequality Really Increased?". Policy Assay. Cato Establish (586).
- U.S. Census Bureau's web-site for income statistics
- NPR.org statistics and background on income inequality in the Us
- Datasets by U.S. Land of low income, very depression income, extremely low income limits
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Household_income_in_the_United_States
0 Response to "House Ways and Means Median Family Income 2017"
Post a Comment